Some techniques:
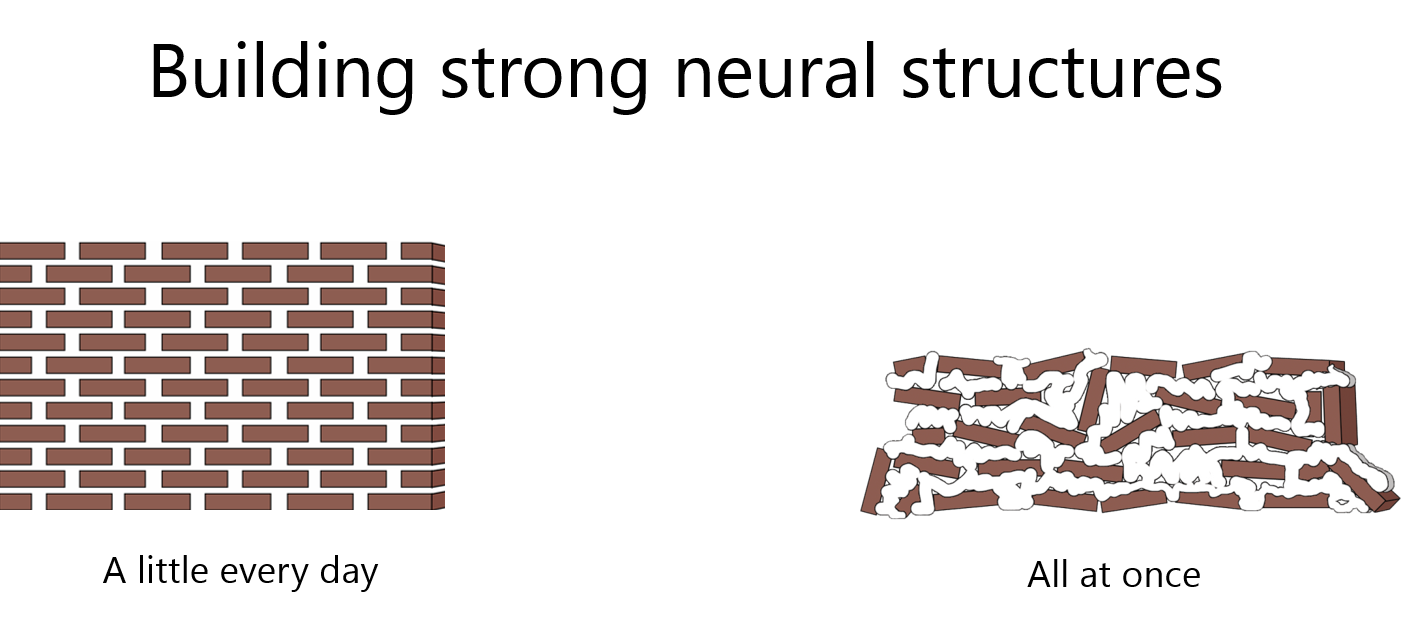
1. Spaced repetition
solving a problem / doing a work without any breaks are not efficient. Here spaced repetition plays a great role. When you are getting frustrated and can’t find any solution then take a small break, and try again or try the next day if its late night. Building walls with cements.
More Here
2. Interleaving
Doing one task continuously in boring and also hinders our learning efficiency. When we are interleaving between tasks, that makes a little space and creates a bond that makes our learning smoother. In example: making a brick wall
More Here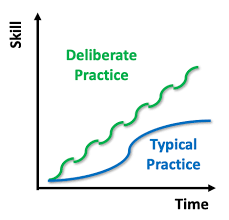
3. Deliberate practice
The more you practice the more that becomes stick with you. Practice again and again makes you more confident and surer about the topic. Test yourself. Don’t afraid of making mistakes
More Here
4. Recalling from the brain
it’s another important thing to make it stick. When we are reading/learning something, it seems we got the whole thing. But the truth is that, it stays with us for some moment and after few seconds when we are engaging in another topic, we almost forget the whole thing. So, one has to recall from the brain and think with a little force
More Here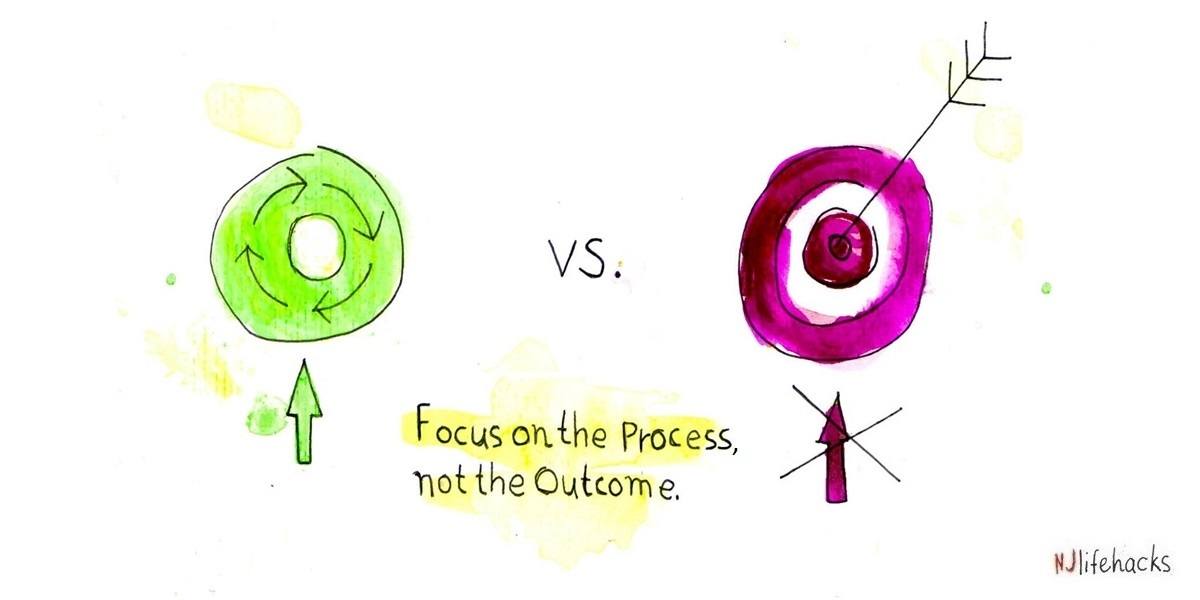
5. Focus on the process
Most of the time we are in an illusion that we focus on the product/ outcome rather than on the process. By focusing on the process, the we get better result and we stay more motivated on that thing
More Here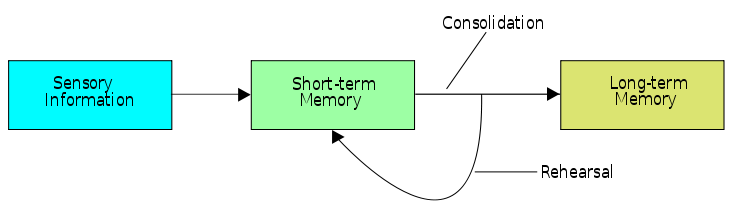
6. Take your time to make it consolidate
we are desperate to learn something as fast as possible, but it takes time to consolidate that information in our brain. The brain processes the info when we are sleeping or doing another work. There’s always ongoing something in the background. The world is moving fast. Although we are progressing fast too. But we are human. It takes time to learn those things
More Here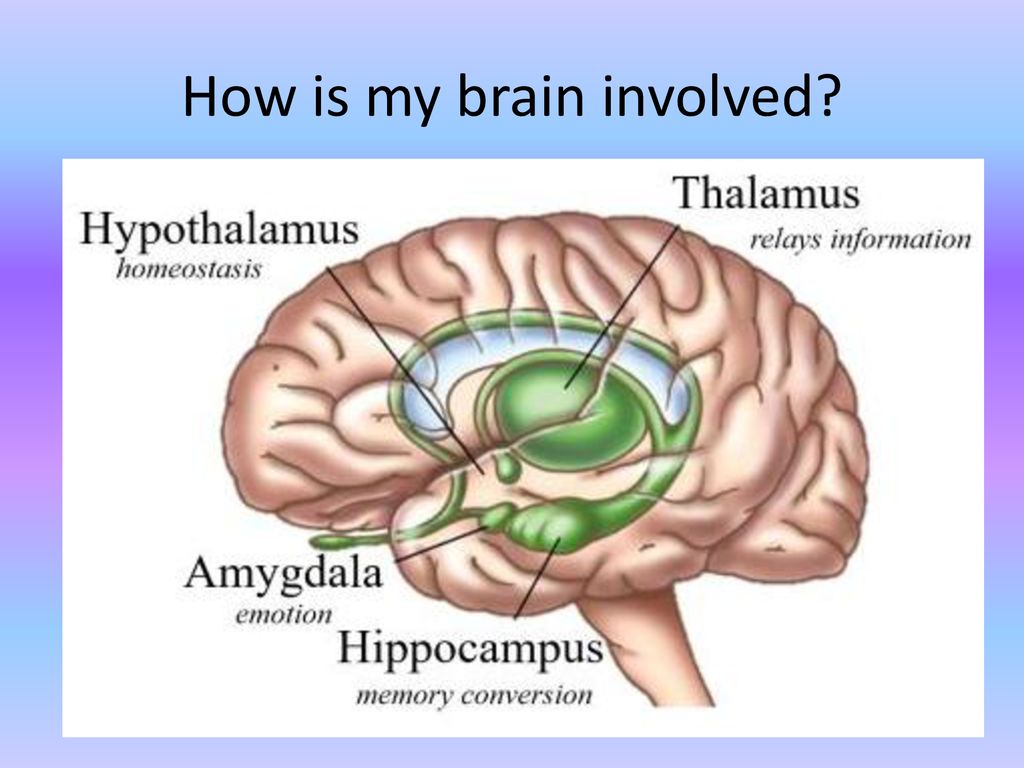
7. Persistency
Stick with it. Don’t give up. The solution will come soon.An
example of persistence is when you try and try to learn a new
skill, never giving up. The act of persisting; stubborn or
enduring continuance.
The Persistence of Memory is a 1931 painting by artist Salvador
Dalí and one of the most recognizable works of Surrealism.
8. Use sense organs in your body
(eye, hand, ear, nose, tongue etc.): an example: think this like you are memorizing your grocery list. When you are trying to gather all the items in your brain without any clue, the total thing gets lost in all of this memory block warehouses. So, you have to think in some imaginary way. Like You are getting bread, egg, milk, fruits and water bottle; you can thing this like, a bread is sitting on a sofa, watching tv. An advertise is going on in TV that shows an egg is bathing with milk and drinking fruit juice, then it come out of bath and takes a water shower to clean itself, I know its funny. But our brain makes it easier to remember
More Here
9. Rewiring the same patterns
When we are learning something, our brain grows through some exercises. The patters in solving one problem may work with another task. When we use the previous experience in another task our brain
More Here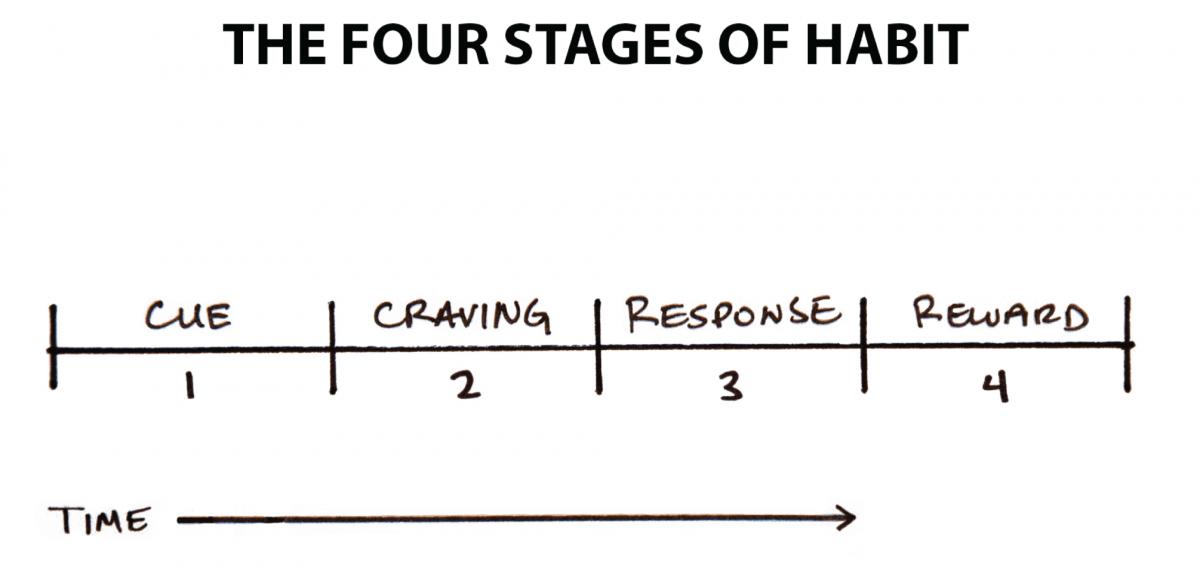
10. Create Habits rather than willpower
willpower is a valuable thing and when we push ourselves too much, it creates the same effect in our brain that also makes us feel like we are being hurt. So, rather than using firing up all day, we should just add a spark into the fuel. The rest of the work will be done by itself
More Here
11. Don’t cram all before exam
it’s bad to create a traffic jam in your brain just by pushing all the things at once
More Here
12. Get enough sleep
sleep is very important, its almost like a restart switch. Our mind refreshes by sleeping and resting our brain
More Here
13. Reward yourself
we are humans, our brains are smart enough to save itself from hard works. It works at its best when there is reward for some task
More Here
14. Tracking your progress
If You Can't Measure It, You Can't Improve It – peter drucker. Write down you progress in some page/note. Try to set goals of that task. You will see very much improvement in that work and avoid procrastination.
More Here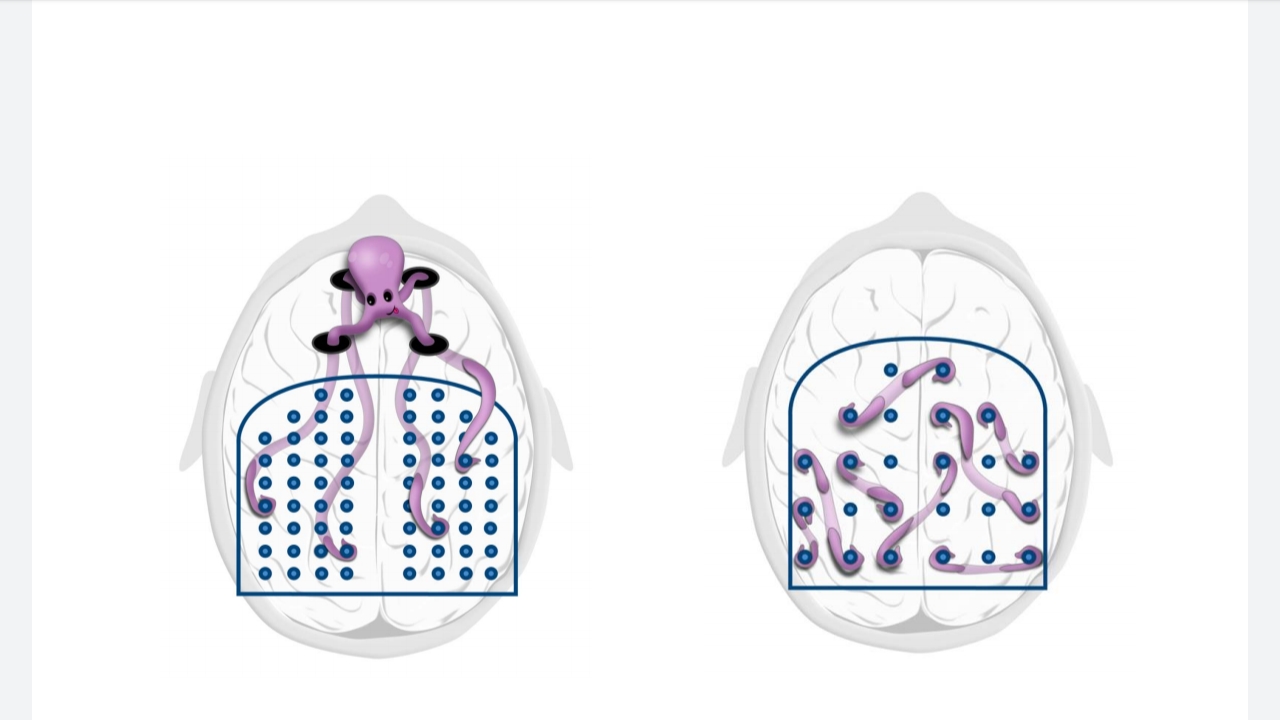
15. Creating chunks
this technique is best of all techniques and the base of almost everything in this course. That’s why I moved it to the bottom of the list
More HereBasic Terms
Teaching someone like a kid
the Feynman technique
Developed by Richard Phillips Feynman Richard an American theoretical physicist. Learn more visually here:
Learn with video(not associated with anything or promoting this video)
Taking a 25-minute time span
Pomodoro technique
Laser focus on that time. Set a timer for 25 minute and take 5-minute break. Learn more here: (not associated with anything or promoting this video)
Learn with video(not associated with anything or promoting this video)
Single task priority:
Deep work
our brain is built for single task at a time. Don’t multitask, rather than choose task one after another
More from an MIT professor:(not associated with anything or promoting this article)
Focus & diffuse mode
This is 2 stages of our thinking. Diffuse mode is like playing a music background.
Learn more here(not associated with anything or promoting this article)
Mind mapping
Create a visual map that makes the big picture clear in your mind and declutter your confusions.r
Memory palace
creating a picture in your mind that makes you remember that topic better
Some errors:
Some creatures:
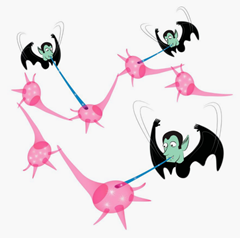
1. Memory sucking vampires
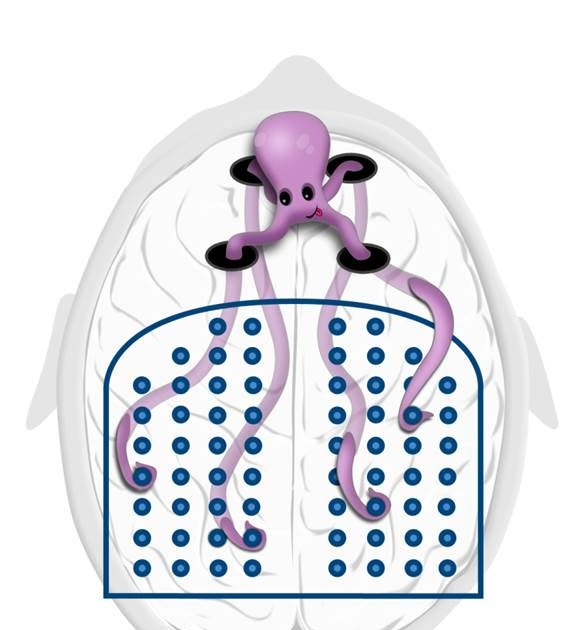
2. Octopus , that connects memory blocks
3. Zombies on our head

4. Flying mule
